-
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 1
[siteid] => 1
[parentid] => 0
[parentstr] => 0,
[infotype] => 0
[classname] => Home
[navname] => Home
[alias] =>
[english] =>
[linkurl] => /
[relinkurl] => index.html
[picurl] =>
[picwidth] =>
[picheight] =>
[colorval] =>
[boldval] =>
[seotitle] => Automotive Lamp suppliers,Led Headlight solutions,Luz Led Para Moto price,Headli
[keywords] => Automotive Lamp suppliers,Led Headlight solutions,
[description] => IV Auto Parts is a Automotive Lamp suppliers, provides Led Headlight solutions,Luz Led Para Moto price,Headlights For Car fittings.
[orderid] => 1
[isnav] => true
[checkinfo] => true
[url] => index.html
[child] => Array
(
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 2
[siteid] => 1
[parentid] => 0
[parentstr] => 0,
[infotype] => 0
[classname] => About Us
[navname] => About Us
[alias] =>
[english] => We Make Fence Idea
[linkurl] => about.php
[relinkurl] => about.html
[picurl] =>
[picwidth] =>
[picheight] =>
[colorval] =>
[boldval] =>
[seotitle] => Car Head Lamp Agencies,vehicle Headlamp Wholesale,car Head Lamp Price; IV Auto P
[keywords] => car head lamp agencies,vehicle headlamp wholesale,
[description] => IV Auto Parts, built in Hongkong and based in mainland China, has specialized
in developing and exporting high quality fencing system since 2009.
[orderid] => 2 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => about.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 10 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Our Culture [navname] => Our Culture [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => about.php?cid=10 [relinkurl] => about-10-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 10 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => about-10-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 11 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Our Team [navname] => Our Team [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => team.php [relinkurl] => team.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] =>
We have been supplying Replacement Headlight assembly,Side Light,Tail Lights,driving Lights,Led Fog,Interior Light,Light Accessories,since 2009, and thanks to the contribution of our professional team, customers across the world thumb up to IV Aut [orderid] => 11 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => team.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 12 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Reference List [navname] => Reference List [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => reference.php [relinkurl] => reference.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 12 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => reference.html [child] => Array ( ) ) ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 3 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 0 [parentstr] => 0, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Warranty [navname] => Warranty [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => warranty.php [relinkurl] => warranty.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Services,Upgrade Headlight Cost; [keywords] => Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Ser [description] => IV Auto Parts Provided For You Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Services,Upgrade Headlight Cost Calculate.
[orderid] => 3 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => warranty.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 13 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => CERTIFICATES [navname] => CERTIFICATES [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => warranty.php?cid=13 [relinkurl] => warranty-13-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => Your partner all the way
At IV Auto Parts we work as a complete supplier: We develop, produce and sell finishing systems and make sure the operators are fully instructed and able to run the Parts.
On top of tha [orderid] => 13 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => warranty-13-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 34 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => FAQ [navname] => FAQ [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => FAQ.php [relinkurl] => FAQ.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 28 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => FAQ.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 33 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Service & After Sales [navname] => Service & After Sale [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => ServiceAndAfterSales.php [relinkurl] => ServiceAndAfterSales.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 29 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => ServiceAndAfterSales.html [child] => Array ( ) ) ) ) [3] => Array ( [id] => 4 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 0 [parentstr] => 0, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Products [navname] => Products [alias] => Products List [english] => Explore Auto Parts Products [linkurl] => products.php [relinkurl] => products.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Headlamp Car For Sale,buy Headlamp,refit Headlight Cost, Head Lamp Fittings; IV [keywords] => IV Auto Parts Provide You With Details Refit Buy [description] => IV Auto Parts Provide You With Details Refit Buy Headlight Cost,head Lamp Fittings For Sale.
[orderid] => 4 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 24 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Headlight assembly [navname] => Headlight assembly [alias] => Headlight assembly [english] => Headlight assembly [linkurl] => products-24-1.html [relinkurl] => products-24-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 22 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-24-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 29 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Taillight Assembly [navname] => Taillight Assembly [alias] => Taillight Assembly [english] => Taillight Assembly [linkurl] => [relinkurl] => products-29-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Taillight Assembly [keywords] => Taillight Assembly,Tail Lights,Tail Lamp,Led Tail [description] => Taillight Assembly,Tail Lamp,Led Tail Lights For Audi [orderid] => 23 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-29-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 25 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Turn Signal Light [navname] => Turn Signal Light [alias] => Turn Signal Light [english] => Turn Signal Light [linkurl] => products-25-1.php [relinkurl] => products-25-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => Turn Signal Light,Side Blinker,Audi Turn Signal Li [description] => Audi Turn Signal Light [orderid] => 24 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-25-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [3] => Array ( [id] => 36 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Alternator [navname] => Alternator [alias] => Alternator [english] => Alternator [linkurl] => products-36-1.php [relinkurl] => products-36-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Alternator For with Audi [keywords] => Alternator For with Audi [description] =>
what does a headlight assembly include
Summary:
Headlights must not be unfamiliar to everyone, it can be said that every day in the use of seeing the car can be seen, then you know the structure of the headlights? What types of headlights are there? Do not know? Then read the following article.
Headlight lighting standards
As the lighting effect of headlights directly affects the operation of night driving and traffic safety, traffic authorities around the world have set out their lighting standards in the form of laws.
The basic requirements for headlamps, which have a special optical structure compared to other lights, are as follows.
The headlamp should provide bright and uniform illumination in front of the vehicle at night so that the driver can identify any obstacle on the road within 100 m.
The headlight should have an anti-glare device to avoid accidents caused by the glare of the other driver when two vehicles meet at night.

The headlight is mainly composed of a bulb, a reflector, and a light distribution mirror. According to the structure of the reflector, headlights can be divided into detachable, semi-enclosed, and enclosed types.
The detachable headlamp has been eliminated due to poor airtightness and the reflector is susceptible to moisture and dust pollution, which reduces the reflecting ability.
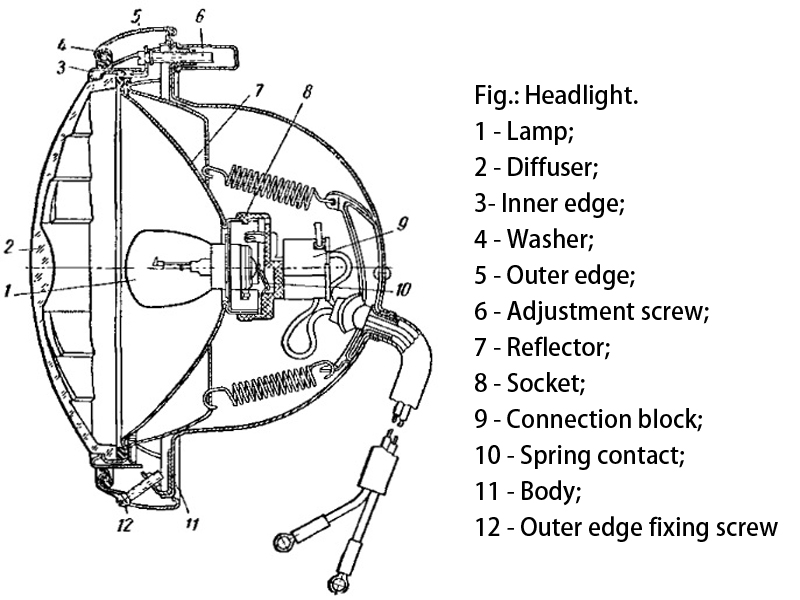
Fig.: Headlight.
1 - Lamp; 2 - Diffuser; h - Inner edge; 4 - Washer; 5 - Outer edge; 6 - Adjustment screw; 7 - Reflector; 8 - Socket; 9 - Connection block; 10 - Spring contact; 11 - Body; 12 - Outer edge fixing screw
The structure of the semi-enclosed headlamp is shown in Fig. 1.
The semi-enclosed headlamp has a sealed front lens and reflector which can be removed from the rear end of the reflector to install the bulb, which has the advantage of being easy to maintain, but the reflector is easily contaminated.
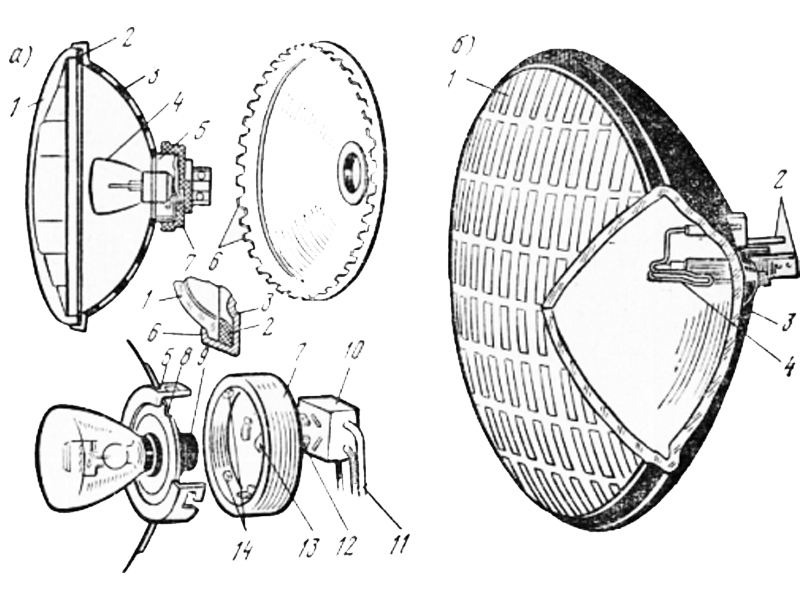
The construction of a fully enclosed headlamp is shown in Fig. 2.
The reflector and front lens are fusion-welded together as a single unit, with the filament welded directly to the base of the reflector, which has the advantage of completely preventing the reflector from being contaminated, but the filament is burnt out and the whole assembly has to be replaced, resulting in high maintenance costs.
The headlamp can be divided into a two-lamp system and a four-lamp system. The four-lamp system consists of a type I lamp with a high beam only and a type II lamp with both a high and low beam.
In the four-light system, the high beam, whether alone or at the same time as the low beam, is in accordance with the regulations.
There are several types of headlamp bulbs, such as inflatable bulbs, tungsten halogen bulbs, and new high-pressure (20 kV) discharge xenon lamps.
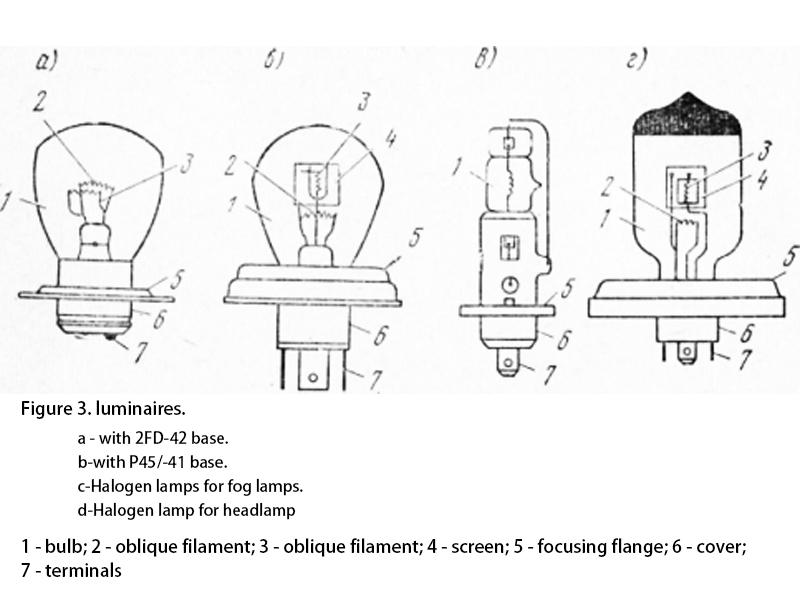
Fig. 3. Lamps: a - with 2FD-42 base; b - with P45/-41 base; c - halogen lamp for fog lamp; d - halogen lamp for a headlamp.
1 - bulb; 2 - oblique filament; 3 - oblique filament; 4 - screen; 5 - focusing flange; 6 - cover; 7 - terminals
Air-filled bulbs
An inflatable bulb is formed by drawing air from a glass bulb and filling it with an inert gas mixture of 86% argon and 14% nitrogen. When the bulb is energized, the filament heats up and the inert gas expands thermally to create a higher pressure, which reduces the evaporation of tungsten and extends the life of the bulb.
Tungsten halogen bulbs
Tungsten halogen bulbs are filled with an inert gas infiltrated with a halogen element, such as iodine or bromine, which prevents the evaporation of the tungsten filament by using the tungsten halogen recycling process.
Although a typical inflatable bulb is filled with a mixture of inert gases, it still does not prevent the tungsten filament from evaporating when heated, and the evaporated tungsten settles on the bulb, making it darker and the light dimmer.
The basic process of the regeneration cycle is that when the bulb is energized, the filament evaporates into gaseous tungsten, which reacts with halogen to form a volatile tungsten halide.
When the tungsten halide diffuses into the high-temperature zone near the filament, it is thermally decomposed so that the tungsten returns to the tungsten filament and the released halogen participates in the next cycle. This type of bulb is small in size and the housing is made of high temperature resistant and mechanically strong quartz glass or hard glass, which can be filled with high-pressure gas. The high operating pressure inside the lamp also inhibits the evaporation of tungsten.
New high-pressure discharge xenon lamps
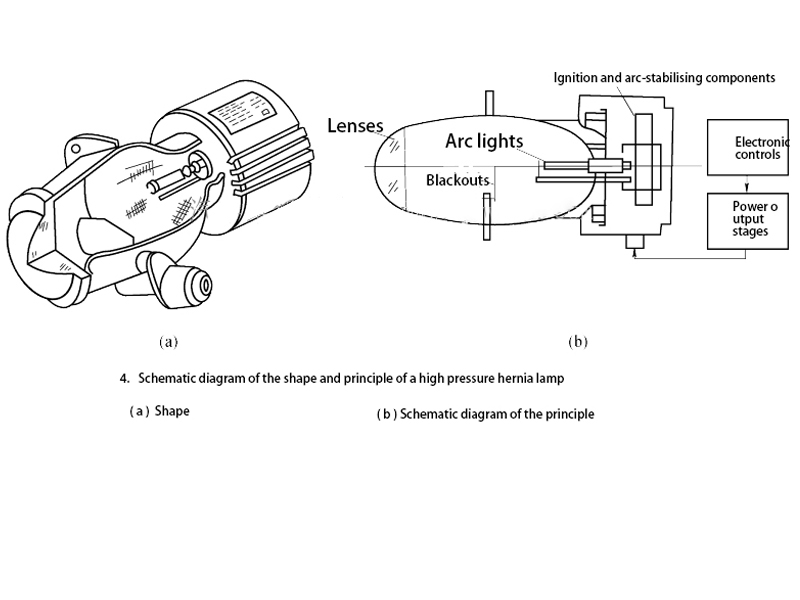
The component system of the new high-pressure discharge xenon lamp consists of an arc lamp assembly, an electronic controller, and a booster, the shape and principle of which are shown in Figure 4.
The color of the light emitted by the lamp is very similar to that of a fluorescent lamp and is about three times brighter than the current halogen bulb, with a life span of up to five times that of a halogen gas bulb.
Instead of the filament of a conventional bulb, the lamp has two electrodes in a quartz tube filled with nitrogen and a trace of metal (or metal halide).
After the electrodes have been added to the arc voltage of tens of thousands of volts, the gas begins to ionize and conduct electricity, the gas atoms are then in an excited state so that the electrons occur in the energy leap and begin to shine, a small amount of mercury vapor evaporates between the electrodes, the light source immediately causes the mercury vapor arc discharge, to be transferred to the halide arc lamp work after the temperature rises.
The headlight bulb is not very luminous and without a reflector, the driver can only identify obstacles 6 m in front of the car.
The role of the reflector
The role of the reflector is to converge the light from the bulb and direct it into the distance. They are made of thin steel, glass, plastic, etc. The surface is a rotating paraboloid, with the inner surface plated with silver, aluminum, or chrome and then polished. Figure 5 shows a reflector reflecting light from a light bulb.
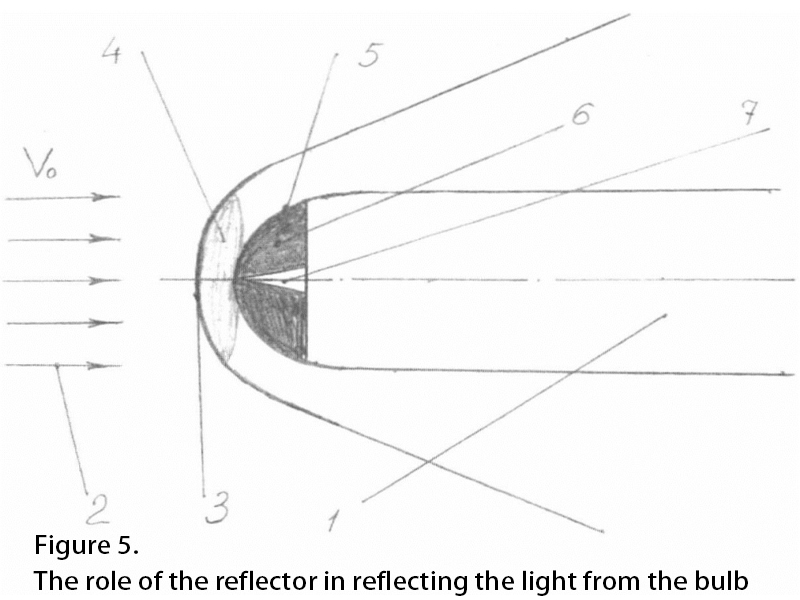
The filament is located at the focal point F. The majority of the light from the filament is directed backward at an angle ω, which is reflected by the reflector into a parallel beam and directed into the distance, increasing the luminosity by a factor of several hundred so that the road surface 100-150 m in front of the vehicle is sufficiently well illuminated. The light from the filament in the 4π - ω range is then scattered in all directions, scattering some of the light to the side and below to illuminate the road surface and curb 5 to 10 m in front of the vehicle.
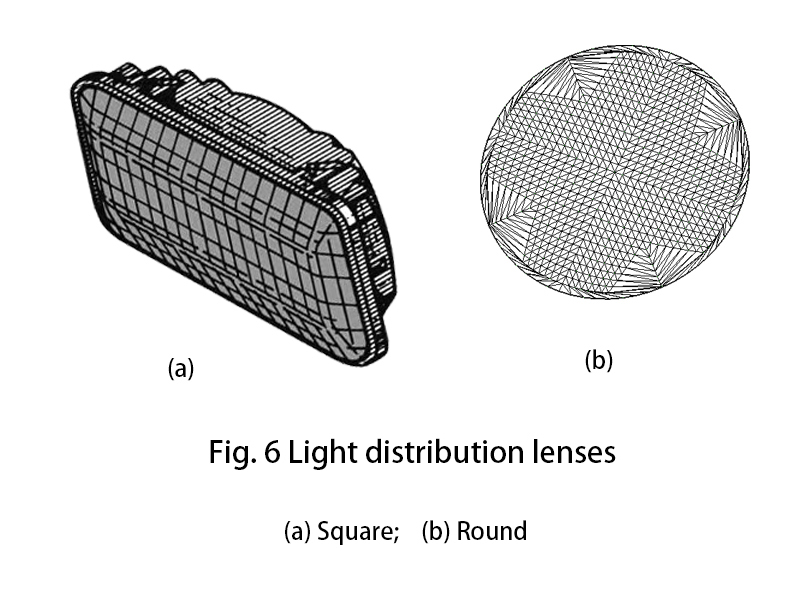
A dispensing mirror is a combination of a lens and a prism, which is generally round or square in shape, see Figure 6.
The role of the light distribution mirror
The role of the light distribution mirror is to refract the parallel beam of light reflected from the reflector so that the road and the curb in front of the car have a good lighting effect.