-
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 1
[siteid] => 1
[parentid] => 0
[parentstr] => 0,
[infotype] => 0
[classname] => Home
[navname] => Home
[alias] =>
[english] =>
[linkurl] => /
[relinkurl] => index.html
[picurl] =>
[picwidth] =>
[picheight] =>
[colorval] =>
[boldval] =>
[seotitle] => Automotive Lamp suppliers,Led Headlight solutions,Luz Led Para Moto price,Headli
[keywords] => Automotive Lamp suppliers,Led Headlight solutions,
[description] => IV Auto Parts is a Automotive Lamp suppliers, provides Led Headlight solutions,Luz Led Para Moto price,Headlights For Car fittings.
[orderid] => 1
[isnav] => true
[checkinfo] => true
[url] => index.html
[child] => Array
(
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 2
[siteid] => 1
[parentid] => 0
[parentstr] => 0,
[infotype] => 0
[classname] => About Us
[navname] => About Us
[alias] =>
[english] => We Make Fence Idea
[linkurl] => about.php
[relinkurl] => about.html
[picurl] =>
[picwidth] =>
[picheight] =>
[colorval] =>
[boldval] =>
[seotitle] => Car Head Lamp Agencies,vehicle Headlamp Wholesale,car Head Lamp Price; IV Auto P
[keywords] => car head lamp agencies,vehicle headlamp wholesale,
[description] => IV Auto Parts, built in Hongkong and based in mainland China, has specialized
in developing and exporting high quality fencing system since 2009.
[orderid] => 2 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => about.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 10 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Our Culture [navname] => Our Culture [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => about.php?cid=10 [relinkurl] => about-10-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 10 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => about-10-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 11 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Our Team [navname] => Our Team [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => team.php [relinkurl] => team.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] =>
We have been supplying Replacement Headlight assembly,Side Light,Tail Lights,driving Lights,Led Fog,Interior Light,Light Accessories,since 2009, and thanks to the contribution of our professional team, customers across the world thumb up to IV Aut [orderid] => 11 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => team.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 12 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Reference List [navname] => Reference List [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => reference.php [relinkurl] => reference.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 12 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => reference.html [child] => Array ( ) ) ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 3 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 0 [parentstr] => 0, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Warranty [navname] => Warranty [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => warranty.php [relinkurl] => warranty.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Services,Upgrade Headlight Cost; [keywords] => Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Ser [description] => IV Auto Parts Provided For You Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Services,Upgrade Headlight Cost Calculate.
[orderid] => 3 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => warranty.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 13 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => CERTIFICATES [navname] => CERTIFICATES [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => warranty.php?cid=13 [relinkurl] => warranty-13-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => Your partner all the way
At IV Auto Parts we work as a complete supplier: We develop, produce and sell finishing systems and make sure the operators are fully instructed and able to run the Parts.
On top of tha [orderid] => 13 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => warranty-13-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 34 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => FAQ [navname] => FAQ [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => FAQ.php [relinkurl] => FAQ.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 28 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => FAQ.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 33 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Service & After Sales [navname] => Service & After Sale [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => ServiceAndAfterSales.php [relinkurl] => ServiceAndAfterSales.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 29 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => ServiceAndAfterSales.html [child] => Array ( ) ) ) ) [3] => Array ( [id] => 4 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 0 [parentstr] => 0, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Products [navname] => Products [alias] => Products List [english] => Explore Auto Parts Products [linkurl] => products.php [relinkurl] => products.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Headlamp Car For Sale,buy Headlamp,refit Headlight Cost, Head Lamp Fittings; IV [keywords] => IV Auto Parts Provide You With Details Refit Buy [description] => IV Auto Parts Provide You With Details Refit Buy Headlight Cost,head Lamp Fittings For Sale.
[orderid] => 4 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 24 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Headlight assembly [navname] => Headlight assembly [alias] => Headlight assembly [english] => Headlight assembly [linkurl] => products-24-1.html [relinkurl] => products-24-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 22 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-24-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 29 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Taillight Assembly [navname] => Taillight Assembly [alias] => Taillight Assembly [english] => Taillight Assembly [linkurl] => [relinkurl] => products-29-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Taillight Assembly [keywords] => Taillight Assembly,Tail Lights,Tail Lamp,Led Tail [description] => Taillight Assembly,Tail Lamp,Led Tail Lights For Audi [orderid] => 23 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-29-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 25 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Turn Signal Light [navname] => Turn Signal Light [alias] => Turn Signal Light [english] => Turn Signal Light [linkurl] => products-25-1.php [relinkurl] => products-25-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => Turn Signal Light,Side Blinker,Audi Turn Signal Li [description] => Audi Turn Signal Light [orderid] => 24 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-25-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [3] => Array ( [id] => 36 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Alternator [navname] => Alternator [alias] => Alternator [english] => Alternator [linkurl] => products-36-1.php [relinkurl] => products-36-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Alternator For with Audi [keywords] => Alternator For with Audi [description] =>
Email:
sales@ivautoparts.com
Tel.: +86 13933893619
How hard is it to replace headlight assembly?
2025-05-27
Summary:
Replacing the headlight assembly on Audi models like the A3, A4, Q5, or TT varies in complexity depending on the specific model, year, and technology involved. Here’s a breakdown of key factors and challenges
How hard is it to replace headlight assembly?
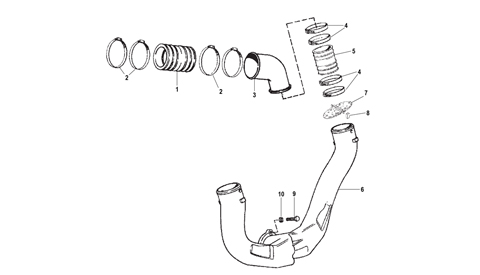
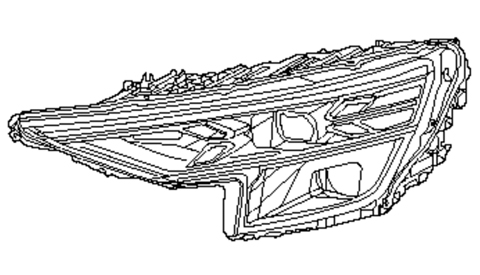
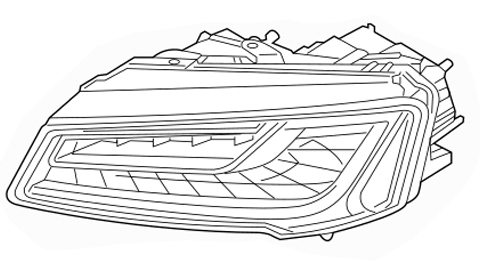
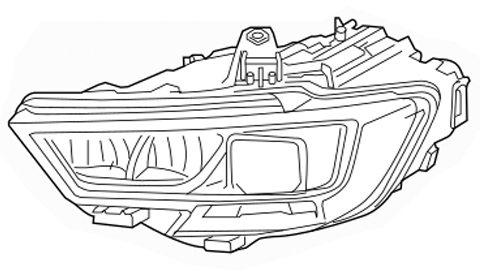
Headlamp Assembly - Audi 8R0-941-003-AP,2013-2015 Audi - 8r0941003ap
Replacing the headlight assembly on Audi models like the A3, A4, Q5, or TT varies in complexity depending on the specific model, year, and technology involved. Here’s a breakdown of key factors and challenges:
1. Model-Specific Complexity
Audi A3: The A3’s modular headlight design often requires replacing the entire assembly if issues arise. For example, some users noted that aftermarket modifications (e.g., LED or laser upgrades) may fail due to incompatibility with the car’s control modules, necessitating a full replacement.
Audi A4: Projects like retrofitting Audi A4’s LED "tear" lights into other vehicles highlight the need for precise wiring, driver modules, and alignment. The process involves disassembling the headlight housing, installing new components, and ensuring proper sealing to prevent moisture ingress.
Audi Q5: Older Q5 models with halogen or xenon headlights may require bulb replacements, but full assembly swaps (e.g., upgrading to LED) often involve coding and calibration for features like auto-leveling.
Audi TT: The TT’s advanced lighting systems (e.g., adaptive headlights with magnetic ride sensors) are prone to faults. Replacing these units may require specialized tools to reset error codes or disable features like the motorized spoiler.
2. Technical Challenges
Wiring and Coding: Modern Audi headlights integrate with the car’s CAN bus system. Installing a new assembly may require coding via tools like VCDS or ODIS to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s electronics. For example, retrofitting LED lights on an A3 might trigger fault codes without proper programming.
Sealing and Alignment: After opening the headlight housing (e.g., for bulb or lens replacements), resealing it with butyl adhesive or silicone is critical to prevent condensation. Misalignment during reassembly can also affect beam patterns.
Component Accessibility: Some models require the removal of bumpers or fenders to access headlight mounting points. For instance, the TT’s compact design may require disassembling front-end components.
3. DIY Feasibility
Basic Bulb Replacement: Swapping halogen bulbs (e.g., in older Q5 or A3 models) is straightforward, often requiring only a screwdriver and patience.
Full Assembly Replacement: This is more involved. For example, retrofitting an A4’s headlight into another car involves cutting the housing, wiring drivers, and securing components with bolts or adhesives—tasks that demand mechanical skill.
Professional Installation Recommended: Professional installation is advised for models with adaptive lighting, matrix LEDs, or dynamic cornering systems to avoid damaging sensitive components or voiding warranties.
4. Cost Considerations
OEM vs. Aftermarket: Genuine Audi assemblies (e.g., A3 LED units) can cost $1,000+ per side, while aftermarket options may lack reliability.
Labor Costs: Dealerships may charge 2–4 hours of labor for coding and installation, especially for complex systems like the TT’s magnetic ride-linked headlights.
Summary
While simple bulb changes are DIY-friendly, replacing entire headlight assemblies on modern Audis often requires technical expertise, coding tools, and careful handling of electronics. For models with advanced features (e.g., adaptive beams or auto-leveling), professional assistance is strongly recommended. Always consult the vehicle’s manual or repair guides for model-specific instructions.
Headlamp Assembly - Audi 8R0-941-003-AP,2013-2015 Audi - 8r0941003ap
Replacing the headlight assembly on Audi models like the A3, A4, Q5, or TT varies in complexity depending on the specific model, year, and technology involved. Here’s a breakdown of key factors and challenges:
1. Model-Specific Complexity
Audi A3: The A3’s modular headlight design often requires replacing the entire assembly if issues arise. For example, some users noted that aftermarket modifications (e.g., LED or laser upgrades) may fail due to incompatibility with the car’s control modules, necessitating a full replacement.
Audi A4: Projects like retrofitting Audi A4’s LED "tear" lights into other vehicles highlight the need for precise wiring, driver modules, and alignment. The process involves disassembling the headlight housing, installing new components, and ensuring proper sealing to prevent moisture ingress.
Audi Q5: Older Q5 models with halogen or xenon headlights may require bulb replacements, but full assembly swaps (e.g., upgrading to LED) often involve coding and calibration for features like auto-leveling.
Audi TT: The TT’s advanced lighting systems (e.g., adaptive headlights with magnetic ride sensors) are prone to faults. Replacing these units may require specialized tools to reset error codes or disable features like the motorized spoiler.
2. Technical Challenges
Wiring and Coding: Modern Audi headlights integrate with the car’s CAN bus system. Installing a new assembly may require coding via tools like VCDS or ODIS to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s electronics. For example, retrofitting LED lights on an A3 might trigger fault codes without proper programming.
Sealing and Alignment: After opening the headlight housing (e.g., for bulb or lens replacements), resealing it with butyl adhesive or silicone is critical to prevent condensation. Misalignment during reassembly can also affect beam patterns.
Component Accessibility: Some models require the removal of bumpers or fenders to access headlight mounting points. For instance, the TT’s compact design may require disassembling front-end components.
3. DIY Feasibility
Basic Bulb Replacement: Swapping halogen bulbs (e.g., in older Q5 or A3 models) is straightforward, often requiring only a screwdriver and patience.
Full Assembly Replacement: This is more involved. For example, retrofitting an A4’s headlight into another car involves cutting the housing, wiring drivers, and securing components with bolts or adhesives—tasks that demand mechanical skill.
Professional Installation Recommended: Professional installation is advised for models with adaptive lighting, matrix LEDs, or dynamic cornering systems to avoid damaging sensitive components or voiding warranties.
4. Cost Considerations
OEM vs. Aftermarket: Genuine Audi assemblies (e.g., A3 LED units) can cost $1,000+ per side, while aftermarket options may lack reliability.
Labor Costs: Dealerships may charge 2–4 hours of labor for coding and installation, especially for complex systems like the TT’s magnetic ride-linked headlights.
Summary
While simple bulb changes are DIY-friendly, replacing entire headlight assemblies on modern Audis often requires technical expertise, coding tools, and careful handling of electronics. For models with advanced features (e.g., adaptive beams or auto-leveling), professional assistance is strongly recommended. Always consult the vehicle’s manual or repair guides for model-specific instructions.