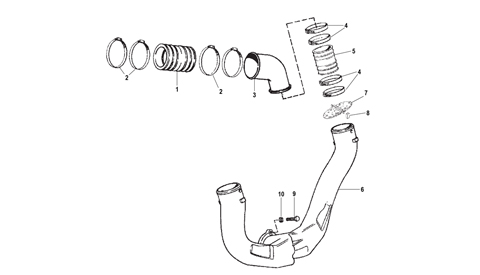
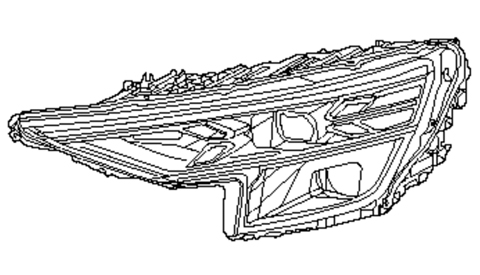
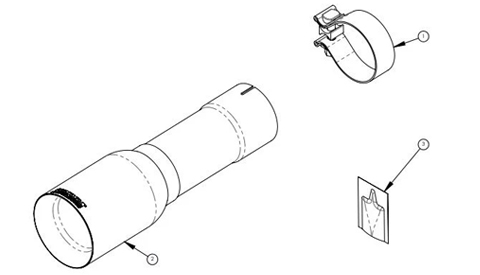
-
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 1
[siteid] => 1
[parentid] => 0
[parentstr] => 0,
[infotype] => 0
[classname] => Home
[navname] => Home
[alias] =>
[english] =>
[linkurl] => /
[relinkurl] => index.html
[picurl] =>
[picwidth] =>
[picheight] =>
[colorval] =>
[boldval] =>
[seotitle] => Automotive Lamp suppliers,Led Headlight solutions,Luz Led Para Moto price,Headli
[keywords] => Automotive Lamp suppliers,Led Headlight solutions,
[description] => IV Auto Parts is a Automotive Lamp suppliers, provides Led Headlight solutions,Luz Led Para Moto price,Headlights For Car fittings.
[orderid] => 1
[isnav] => true
[checkinfo] => true
[url] => index.html
[child] => Array
(
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[id] => 2
[siteid] => 1
[parentid] => 0
[parentstr] => 0,
[infotype] => 0
[classname] => About Us
[navname] => About Us
[alias] =>
[english] => We Make Fence Idea
[linkurl] => about.php
[relinkurl] => about.html
[picurl] =>
[picwidth] =>
[picheight] =>
[colorval] =>
[boldval] =>
[seotitle] => Car Head Lamp Agencies,vehicle Headlamp Wholesale,car Head Lamp Price; IV Auto P
[keywords] => car head lamp agencies,vehicle headlamp wholesale,
[description] => IV Auto Parts, built in Hongkong and based in mainland China, has specialized
in developing and exporting high quality fencing system since 2009.
[orderid] => 2 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => about.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 10 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Our Culture [navname] => Our Culture [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => about.php?cid=10 [relinkurl] => about-10-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 10 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => about-10-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 11 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Our Team [navname] => Our Team [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => team.php [relinkurl] => team.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] =>
We have been supplying Replacement Headlight assembly,Side Light,Tail Lights,driving Lights,Led Fog,Interior Light,Light Accessories,since 2009, and thanks to the contribution of our professional team, customers across the world thumb up to IV Aut [orderid] => 11 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => team.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 12 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 2 [parentstr] => 0,2, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Reference List [navname] => Reference List [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => reference.php [relinkurl] => reference.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 12 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => reference.html [child] => Array ( ) ) ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 3 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 0 [parentstr] => 0, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Warranty [navname] => Warranty [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => warranty.php [relinkurl] => warranty.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Services,Upgrade Headlight Cost; [keywords] => Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Ser [description] => IV Auto Parts Provided For You Halogen Headlamps Solution,Motorcycle Headlamp Services,Upgrade Headlight Cost Calculate.
[orderid] => 3 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => warranty.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 13 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => CERTIFICATES [navname] => CERTIFICATES [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => warranty.php?cid=13 [relinkurl] => warranty-13-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => Your partner all the way
At IV Auto Parts we work as a complete supplier: We develop, produce and sell finishing systems and make sure the operators are fully instructed and able to run the Parts.
On top of tha [orderid] => 13 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => warranty-13-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 34 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => FAQ [navname] => FAQ [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => FAQ.php [relinkurl] => FAQ.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 28 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => FAQ.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 33 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 3 [parentstr] => 0,3, [infotype] => 0 [classname] => Service & After Sales [navname] => Service & After Sale [alias] => [english] => [linkurl] => ServiceAndAfterSales.php [relinkurl] => ServiceAndAfterSales.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 29 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => ServiceAndAfterSales.html [child] => Array ( ) ) ) ) [3] => Array ( [id] => 4 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 0 [parentstr] => 0, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Products [navname] => Products [alias] => Products List [english] => Explore Auto Parts Products [linkurl] => products.php [relinkurl] => products.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Headlamp Car For Sale,buy Headlamp,refit Headlight Cost, Head Lamp Fittings; IV [keywords] => IV Auto Parts Provide You With Details Refit Buy [description] => IV Auto Parts Provide You With Details Refit Buy Headlight Cost,head Lamp Fittings For Sale.
[orderid] => 4 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products.html [child] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 24 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Headlight assembly [navname] => Headlight assembly [alias] => Headlight assembly [english] => Headlight assembly [linkurl] => products-24-1.html [relinkurl] => products-24-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => [description] => [orderid] => 22 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-24-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 29 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Taillight Assembly [navname] => Taillight Assembly [alias] => Taillight Assembly [english] => Taillight Assembly [linkurl] => [relinkurl] => products-29-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Taillight Assembly [keywords] => Taillight Assembly,Tail Lights,Tail Lamp,Led Tail [description] => Taillight Assembly,Tail Lamp,Led Tail Lights For Audi [orderid] => 23 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-29-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 25 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Turn Signal Light [navname] => Turn Signal Light [alias] => Turn Signal Light [english] => Turn Signal Light [linkurl] => products-25-1.php [relinkurl] => products-25-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => [keywords] => Turn Signal Light,Side Blinker,Audi Turn Signal Li [description] => Audi Turn Signal Light [orderid] => 24 [isnav] => true [checkinfo] => true [url] => products-25-1.html [child] => Array ( ) ) [3] => Array ( [id] => 36 [siteid] => 1 [parentid] => 4 [parentstr] => 0,4, [infotype] => 2 [classname] => Alternator [navname] => Alternator [alias] => Alternator [english] => Alternator [linkurl] => products-36-1.php [relinkurl] => products-36-1.html [picurl] => [picwidth] => [picheight] => [colorval] => [boldval] => [seotitle] => Alternator For with Audi [keywords] => Alternator For with Audi [description] =>
Email:
sales@ivautoparts.com
Tel.: +86 13933893619
What type of headlights do Audi use?
2025-02-17
Summary:
Audi employs a diverse range of advanced headlight technologies across its vehicle lineup, combining innovation, safety, and aesthetic appeal. Below is a detailed breakdown of the types of headlights Audi uses, along with their key features and applicatio
Audi employs a diverse range of advanced headlight technologies across its vehicle lineup, combining innovation, safety, and aesthetic appeal. Below is a detailed breakdown of the types of headlights Audi uses, along with their key features and applications:
1. Matrix LED Headlights
Technology Overview:
Matrix LED headlights utilize an array of individually controlled LEDs to dynamically adjust illumination patterns. A frontfacing camera detects other vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs, dimming specific segments of the light beam to avoid glare while maintaining optimal visibility. This system can track up to eight vehicles simultaneously.
Applications:Found in models like the Audi A4L, A6L (C8), A8L (D4), Q7, and Q8 .
Offers automatic highbeam adjustment, adaptive lighting for curves, and dynamic turn signals.
Advantages: Enhances safety by preventing blinding other drivers.
Provides precise illumination, improving nighttime visibility.
2. Laser Headlights
Technology Overview:
Laser headlights combine laser diodes with matrix LED technology, achieving a remarkable 600meter illumination range (twice the distance of traditional LED high beams). They activate only at high speeds to extend visibility without energy waste.
Applications: Featured in highend models like the Audi Q8 and etron GT .
Advantages: Exceptional energy efficiency (1.7x more efficient than LEDs) and longrange illumination.
Integrated with safety systems to highlight pedestrians near the road via flashing marker lights.
3. Digital Matrix LED (DMD Technology)
Technology Overview:
Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) technology uses a chip with 1.3 million micromirrors (each smaller than a hair’s width) to project precise light patterns. This allows dynamic "light carpet" projections on the road, such as lane guidance or hazard warnings.
Applications: Debuted in the Audi etron and extended to newer electric models like the Q6 etron .
Advantages: Enables interactive lighting (e.g., projecting animations or safety symbols).
Enhances driver safety through adaptive light distribution.
4. Xenon Headlights
Technology Overview:
Xenon (HID) headlights use gas discharge lamps with tungsten electrodes and xenon gas, producing a bright, daylightlike beam. They consume 20% less energy than halogen bulbs and have a longer lifespan.
Applications: Historically used in models like the Audi A4 B8 and older generations of the A6 and Q5 .
Advantages: Superior brightness and energy efficiency compared to halogen.
Mercuryfree design for environmental safety.
5. OLED Tailights (Complementary Technology)
While primarily used for taillights, Audi’s secondgeneration digital OLED technology (with 360 segments per panel) enables interactive functions, such as displaying warning signals to nearby drivers.
6. Intelligent Interaction Features
Audi integrates headlights with advanced driverassistance systems (ADAS):
CartoX Communication: Headlights in the Q6L etron communicate with other vehicles and infrastructure to project warnings.
Pedestrian Protection: Marker lights flash to alert drivers and pedestrians of potential hazards.
Future Innovations
For 2025, Audi plans to introduce nextgen matrix LED headlights in the redesigned Q3, featuring programmable lighting effects and enhanced adaptability. The brand continues to prioritize lighting as a core element of its design and safety philosophy.
1. Matrix LED Headlights
Technology Overview:
Matrix LED headlights utilize an array of individually controlled LEDs to dynamically adjust illumination patterns. A frontfacing camera detects other vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs, dimming specific segments of the light beam to avoid glare while maintaining optimal visibility. This system can track up to eight vehicles simultaneously.
Applications:Found in models like the Audi A4L, A6L (C8), A8L (D4), Q7, and Q8 .
Offers automatic highbeam adjustment, adaptive lighting for curves, and dynamic turn signals.
Advantages: Enhances safety by preventing blinding other drivers.
Provides precise illumination, improving nighttime visibility.
2. Laser Headlights
Technology Overview:
Laser headlights combine laser diodes with matrix LED technology, achieving a remarkable 600meter illumination range (twice the distance of traditional LED high beams). They activate only at high speeds to extend visibility without energy waste.
Applications: Featured in highend models like the Audi Q8 and etron GT .
Advantages: Exceptional energy efficiency (1.7x more efficient than LEDs) and longrange illumination.
Integrated with safety systems to highlight pedestrians near the road via flashing marker lights.
3. Digital Matrix LED (DMD Technology)
Technology Overview:
Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) technology uses a chip with 1.3 million micromirrors (each smaller than a hair’s width) to project precise light patterns. This allows dynamic "light carpet" projections on the road, such as lane guidance or hazard warnings.
Applications: Debuted in the Audi etron and extended to newer electric models like the Q6 etron .
Advantages: Enables interactive lighting (e.g., projecting animations or safety symbols).
Enhances driver safety through adaptive light distribution.
4. Xenon Headlights
Technology Overview:
Xenon (HID) headlights use gas discharge lamps with tungsten electrodes and xenon gas, producing a bright, daylightlike beam. They consume 20% less energy than halogen bulbs and have a longer lifespan.
Applications: Historically used in models like the Audi A4 B8 and older generations of the A6 and Q5 .
Advantages: Superior brightness and energy efficiency compared to halogen.
Mercuryfree design for environmental safety.
5. OLED Tailights (Complementary Technology)
While primarily used for taillights, Audi’s secondgeneration digital OLED technology (with 360 segments per panel) enables interactive functions, such as displaying warning signals to nearby drivers.
6. Intelligent Interaction Features
Audi integrates headlights with advanced driverassistance systems (ADAS):
CartoX Communication: Headlights in the Q6L etron communicate with other vehicles and infrastructure to project warnings.
Pedestrian Protection: Marker lights flash to alert drivers and pedestrians of potential hazards.
Future Innovations
For 2025, Audi plans to introduce nextgen matrix LED headlights in the redesigned Q3, featuring programmable lighting effects and enhanced adaptability. The brand continues to prioritize lighting as a core element of its design and safety philosophy.